Mechanism
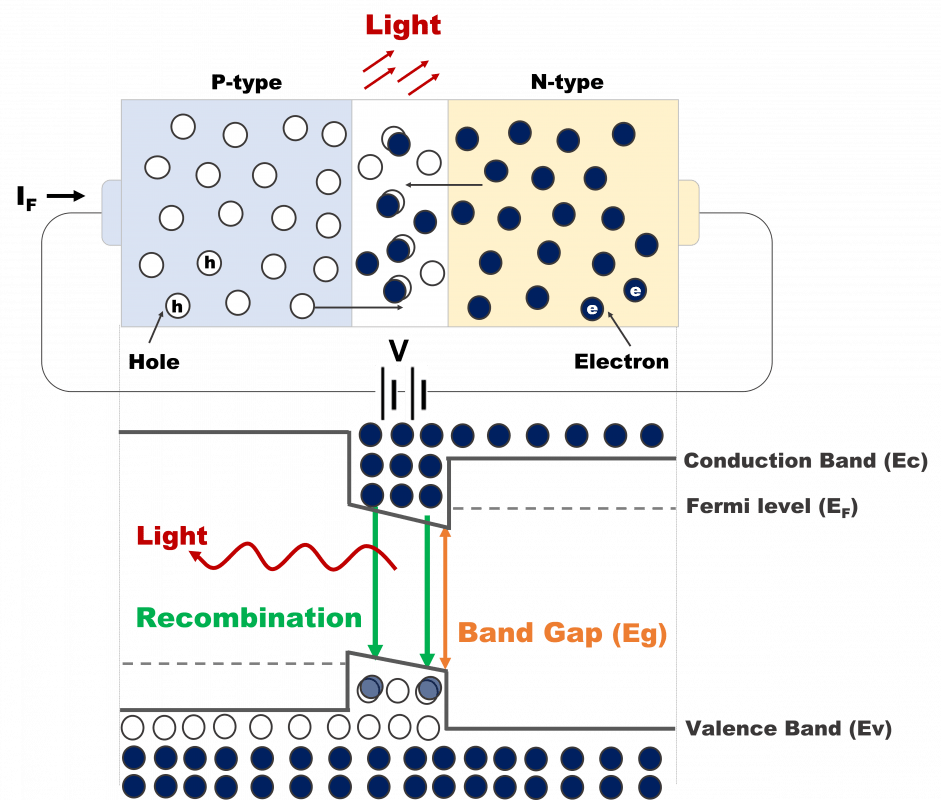
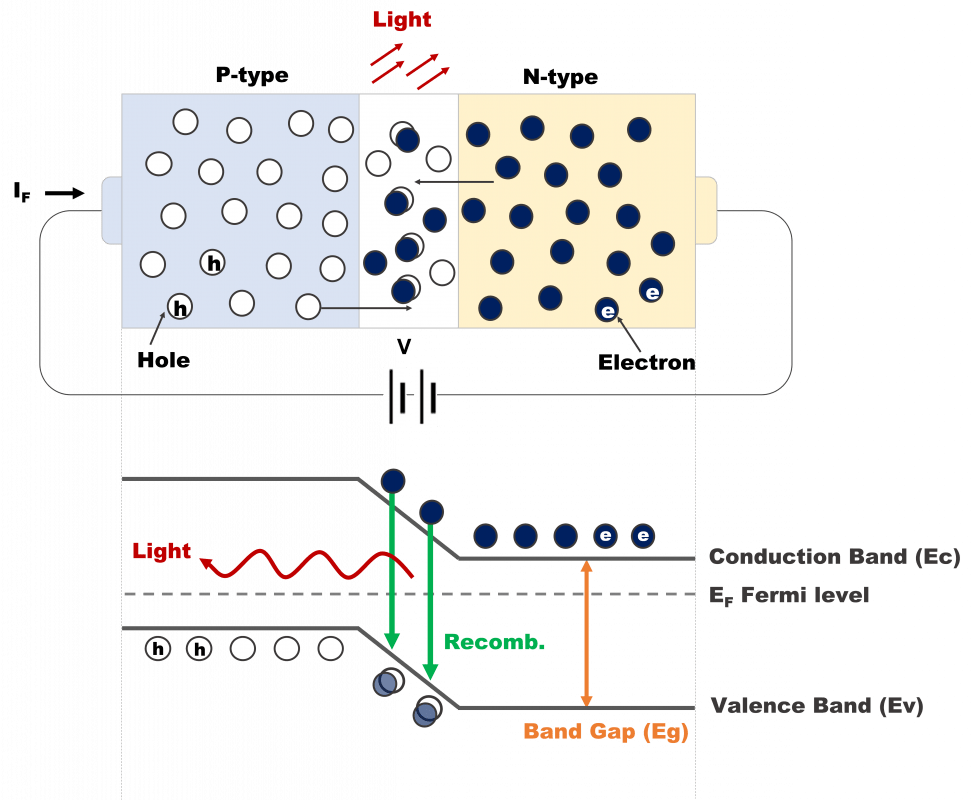
Most of the LED are direct band gap materials and mainly composed of P-type and N-type semiconductors. When a forward bias is externally applied, the holes and electrons flow to N-electrode and P-electrode by electrode field respectively. It will release a certain energy due to electrons and holes recombination at the PN junction. If the energy is released in the form of photons, it will produce the ultraviolet light, visible and infrared light according to different energy gap of materials.
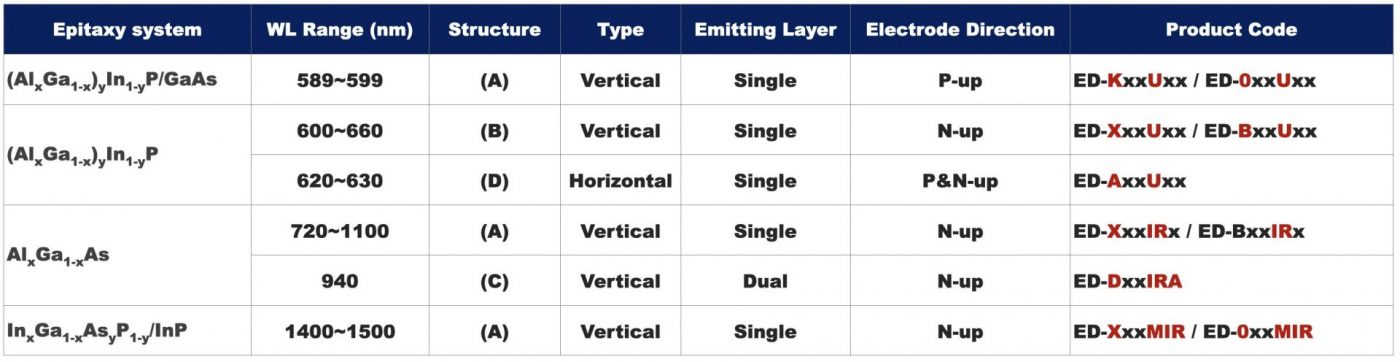
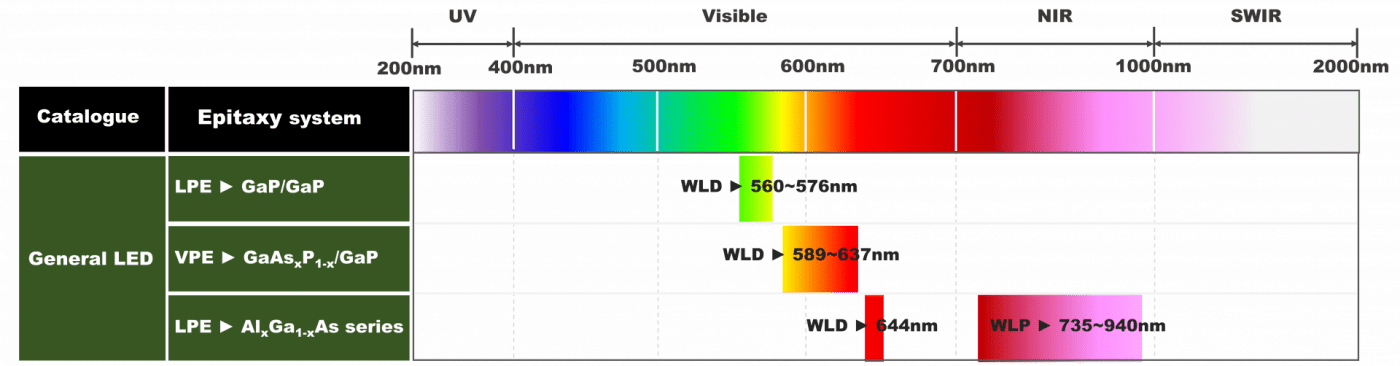
General LED Series (TASC)
These types of epitaxy are produced by liquid phase epitaxy or vapor phase epitaxy. These kind of products have good uniformity in optical power (mW) and light intensity (cd) which can adapt to indoor products. Thus, the visible light is commonly used in small decoration lighting and indicator. The infrared light is for signal transmission in coupler and monitor.
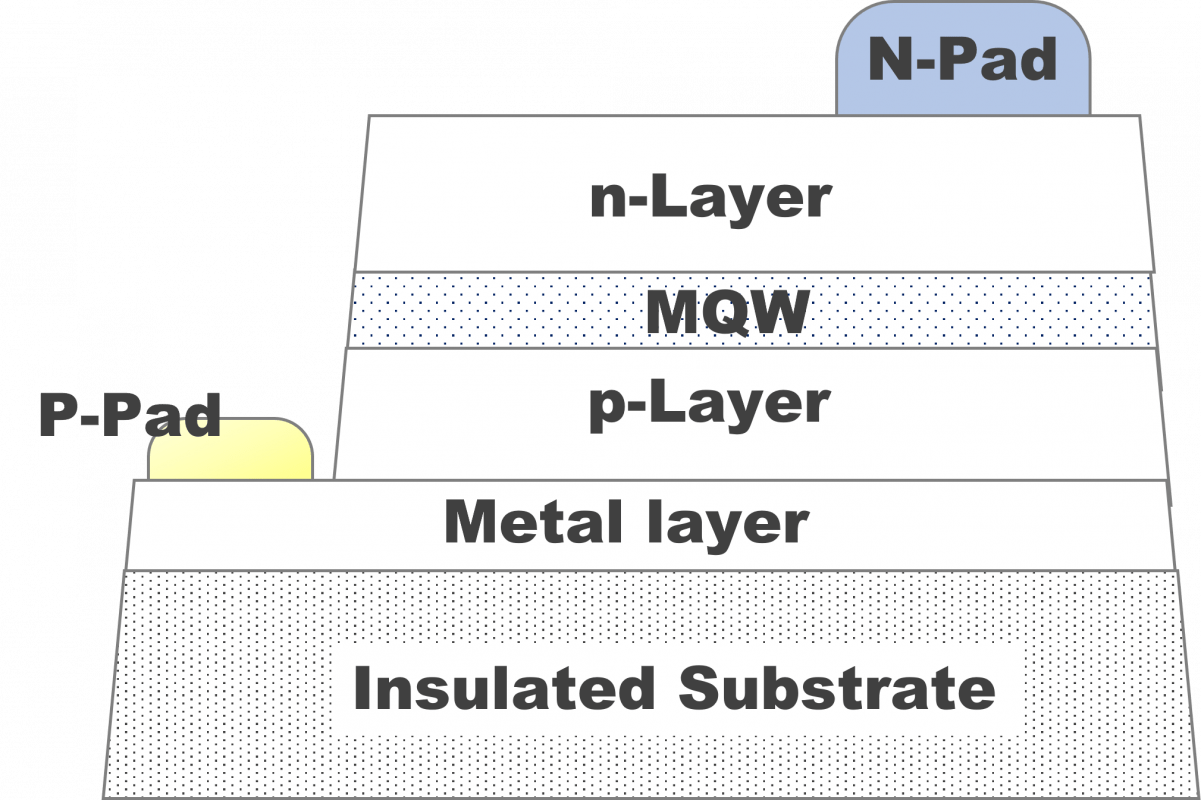
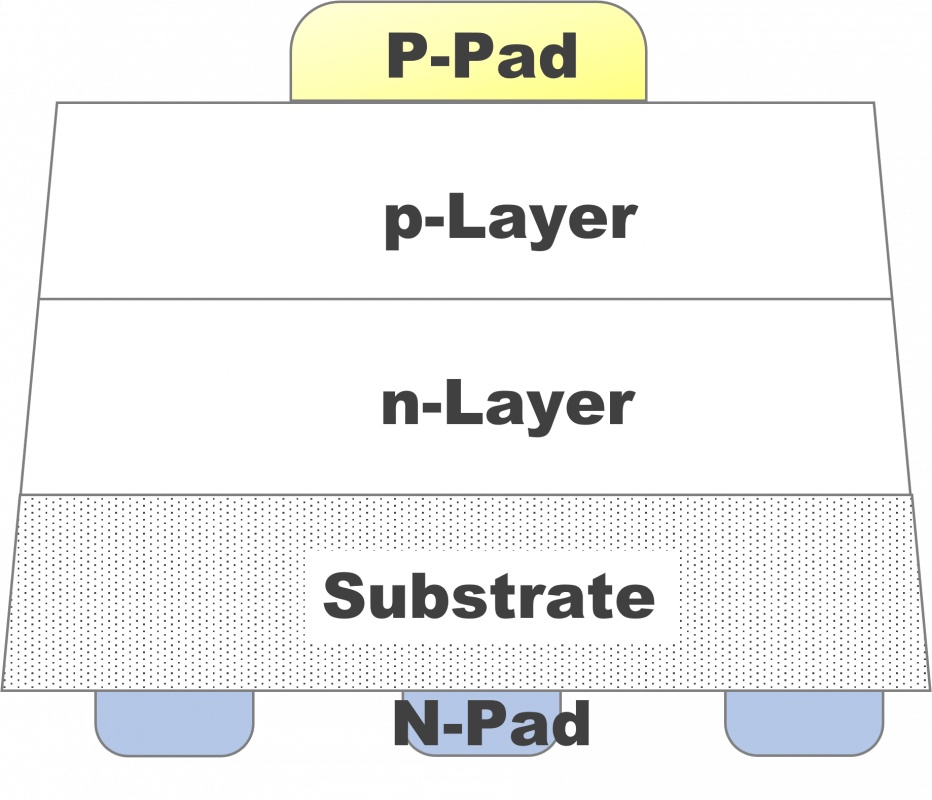
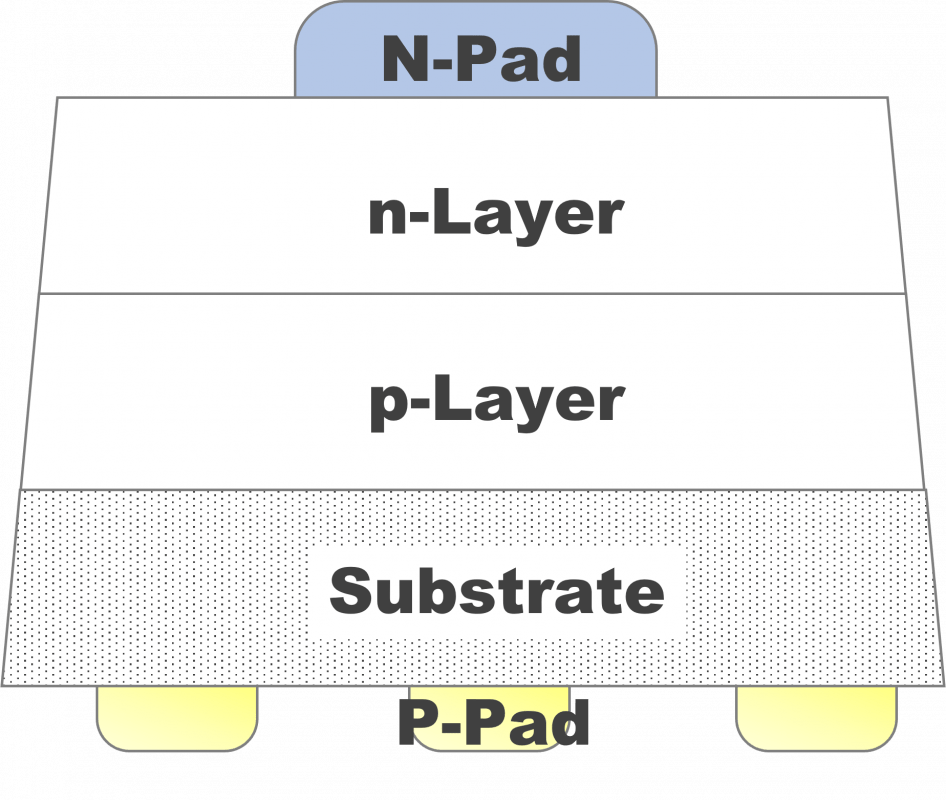
Chip structure
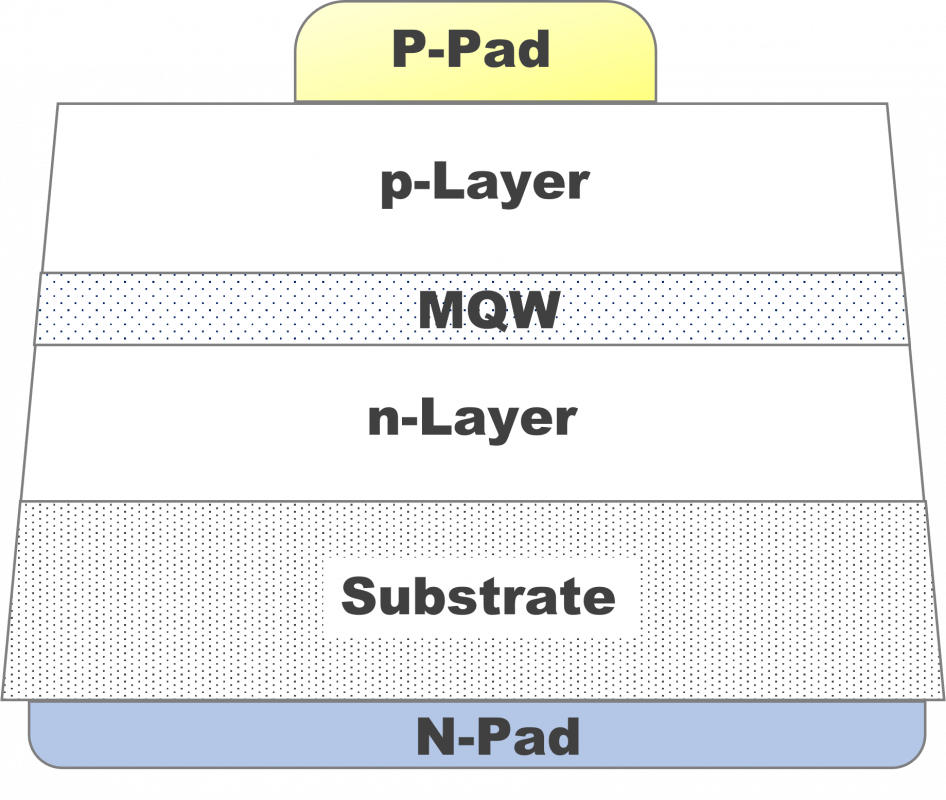
Structure (A)
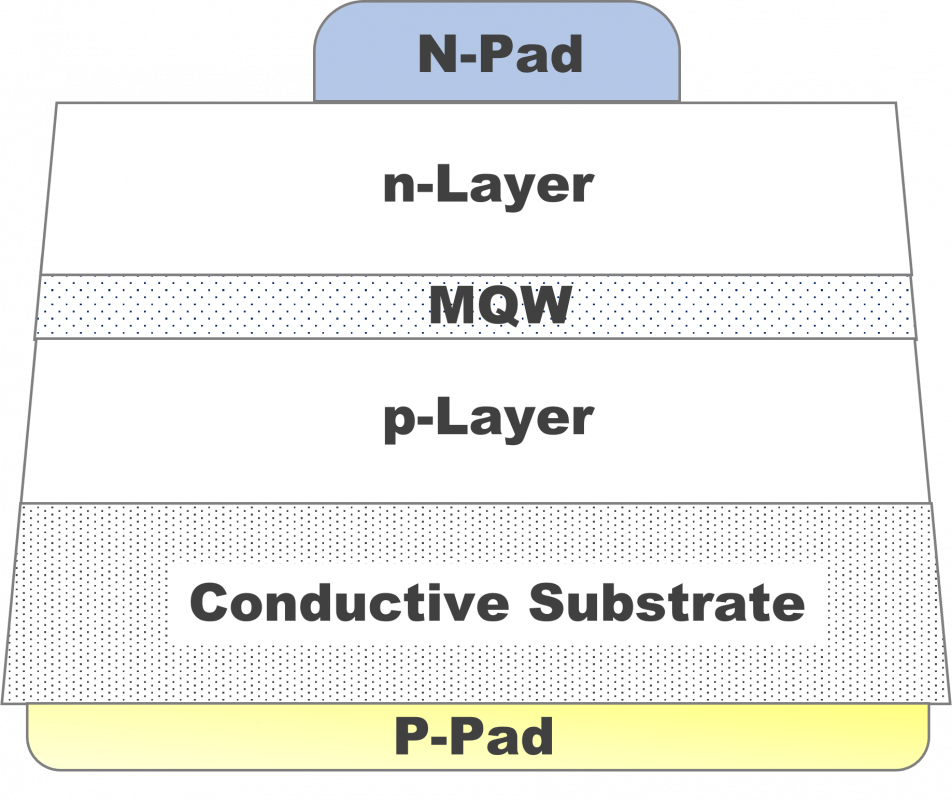
Structure (B)
Structure (C)
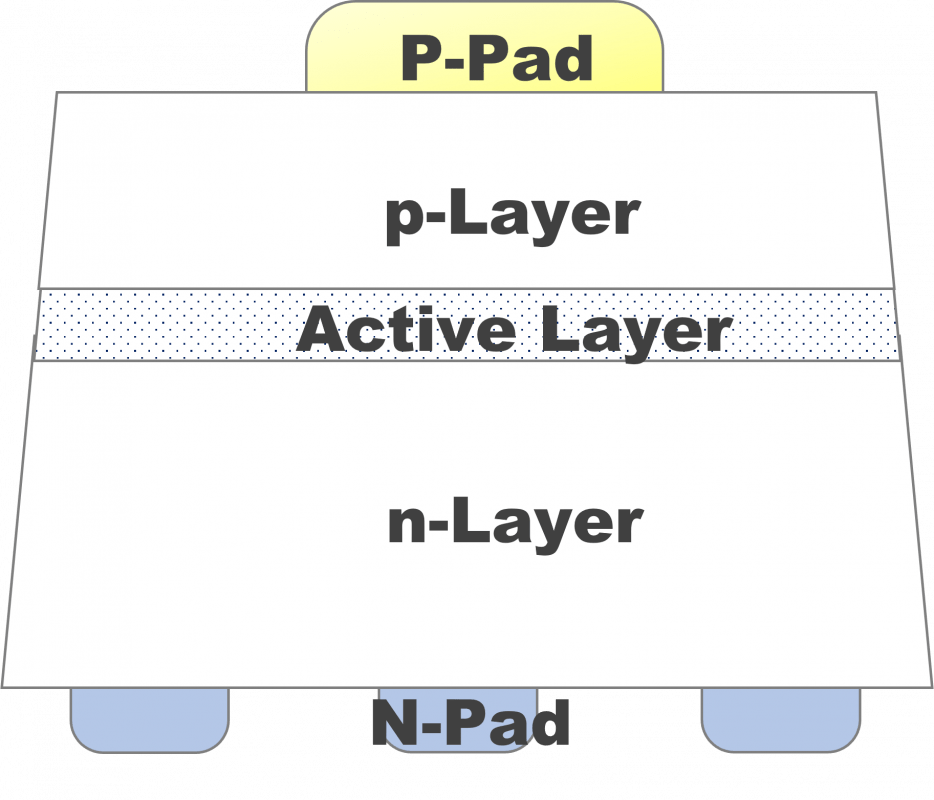
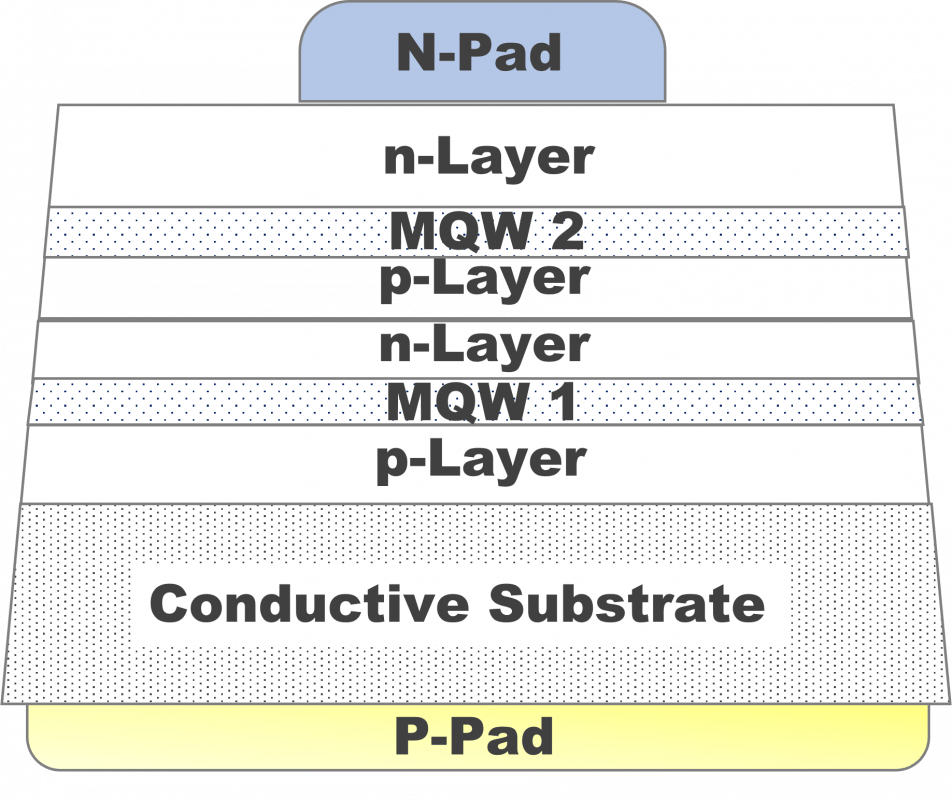
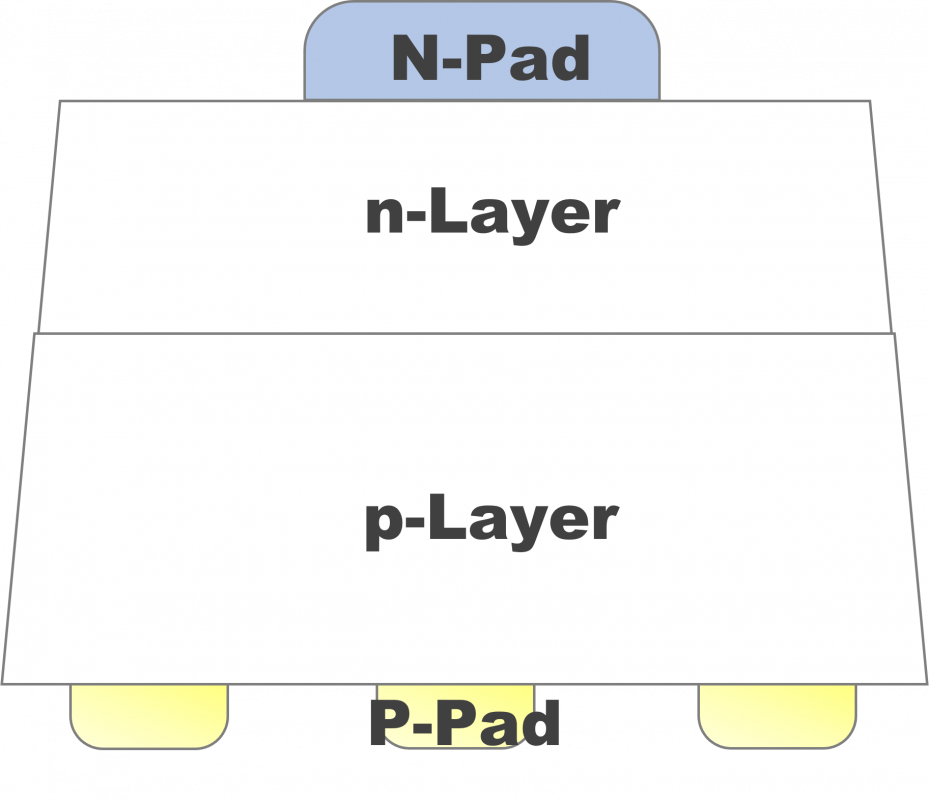
Structure (D)
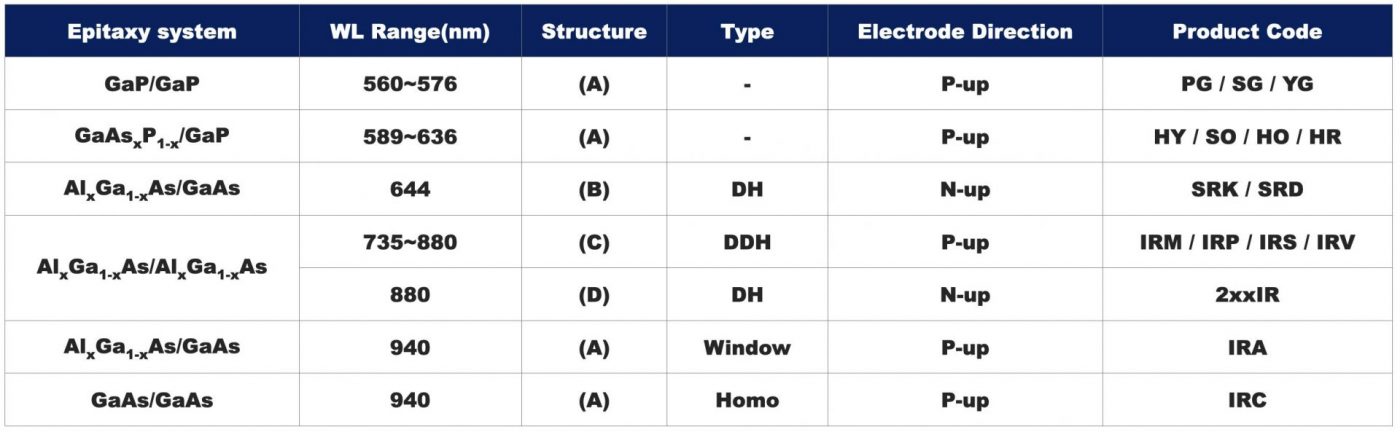
Parameters Explanation
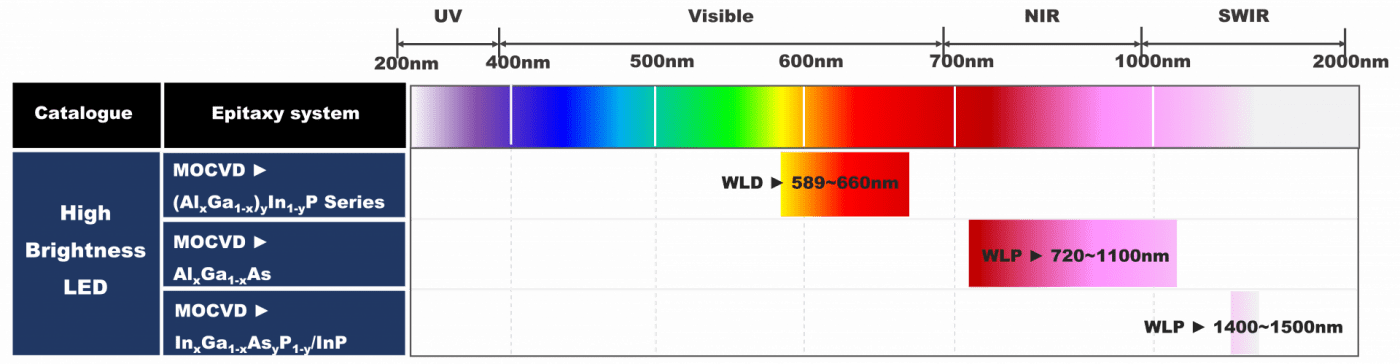
Dominant wavelength (WLD) : The wavelength which is most closest to vision color of human eye
Peak wavelength (WLP) : The wavelength with highest intensity in light spectrum
Full width at half maximum (FWHM) : The full width of wavelength distance between two points at which the function reaches half its maximum value on spectrum
Radiant Power : The total optical power value per unit time ; The unit is Watt
Luminous Intensity : The illumination of indicated light direction in unit solid angle ; The unit is Candela or cd